Hydrogen production - Hydrogen production by electrolysis of water
- As a clean and efficient secondary energy, hydrogen energy is of great significance for building a clean, low-carbon, safe and efficient energy system. Under the action of direct current, the water electrolysis hydrogen production technology decomposes water into pure hydrogen and pure oxygen. As an energy carrier, hydrogen can realize the recycling of carbon-free energy, and can efficiently utilize the fluctuating renewable energy power through the method of "electricity-hydrogen-electricity (or chemical raw materials)", which is both green and efficient.
- Hydrogen production from water electrolysis mainly includes three technical routes: alkaline electrolysis (AWE), proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis, and solid oxide (SOEC) electrolysis.
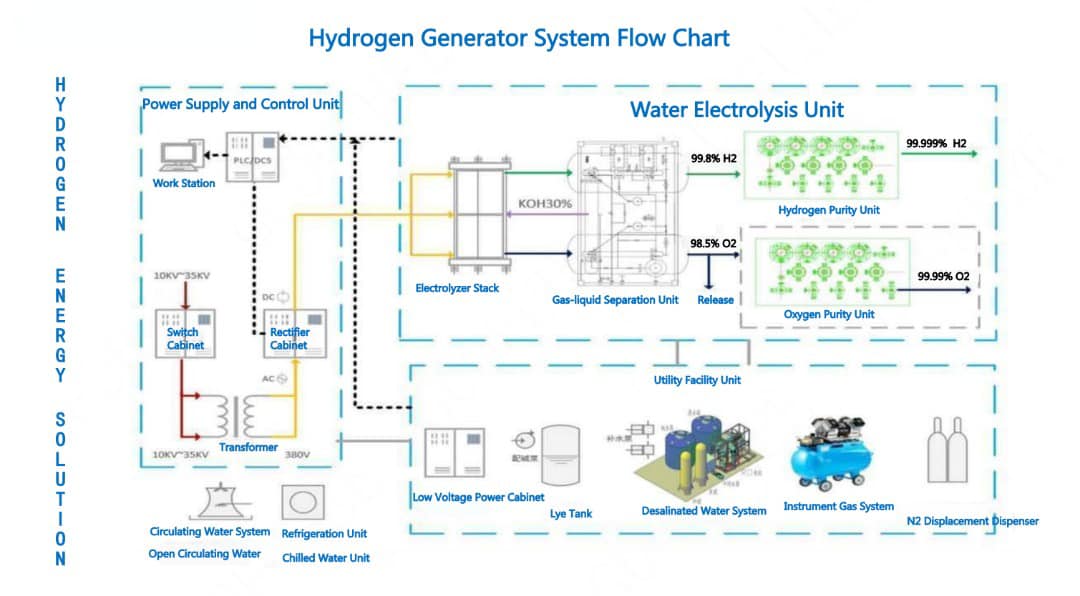
- The technical route of hydrogen production from alkaline electrolysis water is mature, the equipment cost is low, and it is more economical. Hydrogen production by water electrolysis in alkaline liquid electrolyzers The alkaline liquid water electrolysis technology uses KOH and NaOH aqueous solutions as electrolytes, such as asbestos cloth as a diaphragm, and under the action of direct current, water is electrolyzed to generate hydrogen and oxygen.
- PEM water Electrolyzer uses solid proton exchange membrane PEM as electrolyte and pure water as reach tant. Due to the low hydrogen permeability of the PEM electrolyte, the hydrogen produced has high purity, and only water vapor needs to be removed, the process is simple, and the safety is high; The volume is more compact; the pressure regulation range is large, and the hydrogen output pressure can reach several megapascals, adapting to the rapidly changing renewable energy power input. The practical SPE is the proton exchange membrane (PEM), which is also called PEM electrolysis.
- Solid oxide electrolysis cell (SOEC) is an advanced electrochemical energy conversion device, which can utilize the electric and thermal energy generated by clean primary energy, and use H2O and/or CO2 as raw materials to efficiently electrolyze hydrogen or hydrocarbon fuels. Large-scale energy energy-efficient version and storage. This technology has the characteristics of high efficiency, simplicity, flexibility, and environmental friendliness, and is currently a research hotspot in the international energy field.




